Plant extraction is a crucial process used to isolate desired compounds from botanical materials. One of the most effective techniques for this purpose is the use of a rotary evaporator. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on plant extraction using a rotary evaporator, including its working principle, applications, and benefits. Additionally, a case study will be presented to highlight the practical application of this technique.
I. Understanding the Rotary Evaporator
The rotary evaporator, also known as a rotovap, is a laboratory instrument widely employed for efficient solvent evaporation in chemical and pharmaceutical industries. It consists of a rotating flask, a condenser, a vacuum system, and a water bath. The key principle behind its operation is the gentle removal of solvents from plant extracts, leaving behind concentrated substances of interest.
II. The Working Principle of Rotary Evaporator
A. Evaporation Process
1. Initial Setup
To start, place the plant extract in a round-bottomed flask and attach it to the rotary evaporator, ensuring airtight conditions by sealing the system.
2. Rotation and Heating
Setting the round-bottomed flask in motion causes the liquid inside to rotate, while simultaneously heating the water bath to maintain a constant temperature for facilitating solvent evaporation.
3. Vacuum Assistance
The vacuum system connected to the rotary evaporator reduces the pressure inside the flask, lowering the boiling point of the solvent. This accelerates the evaporation process while minimizing heat damage to the delicate compounds.
B. Condensation Process
1. Cold Finger or Liebig Condenser
As the solvent evaporates, it rises as vapor and travels through the condenser. The condenser, usually a cold finger or Liebig condenser, cools down the vapor, causing it to condense back into a liquid state.
2. Collection of Distillate
The condensed liquid collects in a separate container, away from the plant material. This liquid is enriched with the desired compounds and serves as the final product.

III. Applications of Rotary Evaporator in Plant Extraction
The use of a rotary evaporator for plant extraction offers a wide range of applications across various industries. Some notable applications include:
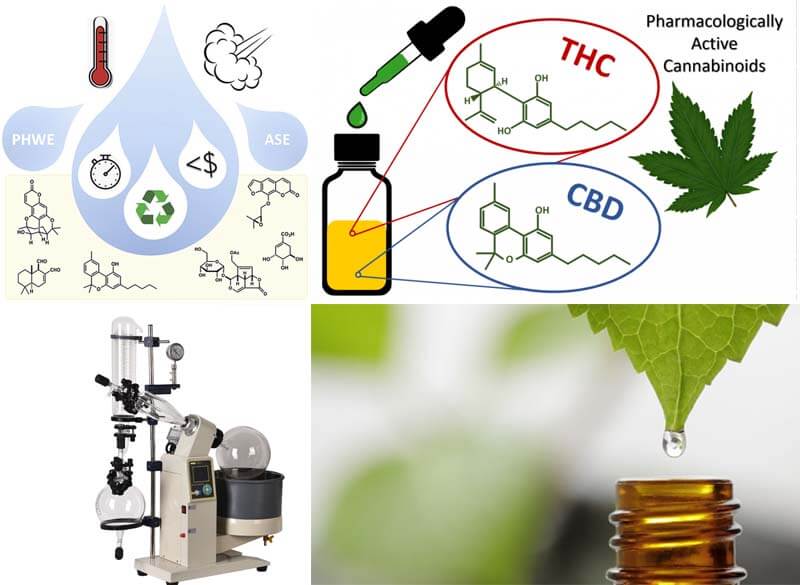
A. Essential Oil Extraction
Rotary evaporators are extensively employed in the extraction of essential oils from aromatic plants. The technique allows for the isolation of volatile compounds responsible for the characteristic fragrance and therapeutic properties of these oils.
B. Natural Product Isolation
Many plants contain bioactive compounds with potential pharmaceutical applications. Rotary evaporators assist in extracting and concentrating these natural products, which researchers can subsequently process for drug development or herbal medicine production.
C. Cannabinoid Extraction
Due to the growing interest in medicinal cannabis, researchers utilize rotary evaporators to extract cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, from the plant material. This technique enables the production of highly concentrated extracts for medicinal purposes.
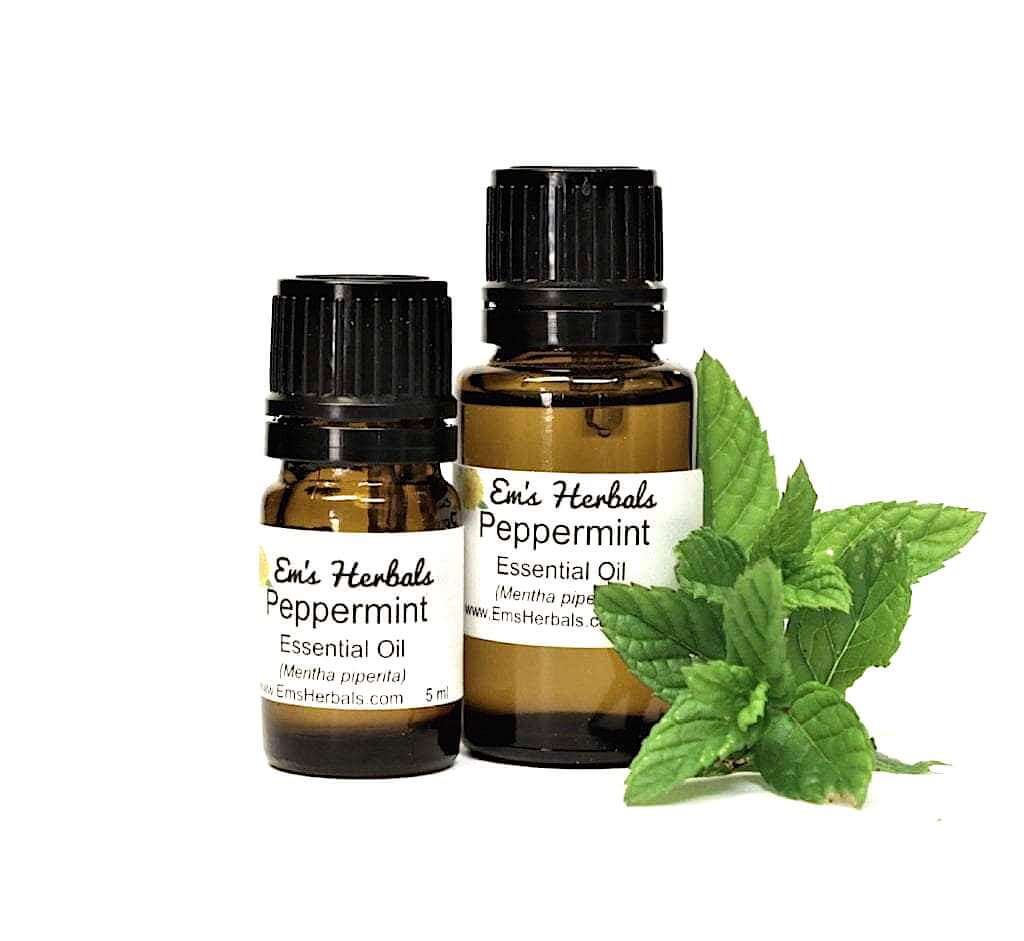
IV. Case: Mentha piperita (Peppermint) Essential Oil Extraction
To illustrate the practical application of plant extraction using a rotary evaporator, let’s consider the example of Mentha piperita (peppermint) essential oil extraction.
A. Experimental Setup
Researchers collected fresh peppermint leaves and performed steam distillation for the initial extraction. Researchers then processed the resulting hydrosol using a rotary evaporator to obtain the concentrated essential oil.
B. Rotary Evaporator Parameters
A rotary evaporator with a water bath temperature of 50°C and a vacuum pressure of 100 mbar was employed. The flask rotation speed was set to 120 revolutions per minute (RPM) to ensure efficient evaporation.
C. Results and Observations
The rotary evaporators successfully separated the peppermint essential oil from the hydrosol, resulting in a highly concentrated extract. The extracted oil had a density of 2.5% and possessed the characteristic aroma and flavor associated with peppermint.

V. Advantages of Rotary Evaporators in Plant Extraction
The use of a rotary evaporator offers several advantages over other extraction methods:
A. Time Efficiency
The rotary evaporator allows for faster extraction due to its efficient evaporation process. It significantly reduces the time required for solvent removal, enabling quicker isolation of desired compounds.
B. Improved Yield and Purity
By operating under reduced pressure, the rotary evaporators minimizes the exposure of heat-sensitive compounds to high temperatures. This preserves the integrity of the extracted substances, resulting in higher yields and improved purity.
C. Versatility and Scalability
Rotary evaporators are adaptable to a wide range of plant materials and can accommodate both small-scale and large-scale extractions. This flexibility makes them suitable for various research, development, and production needs.
Plant extraction using a rotary evaporator is a valuable technique in the isolation and concentration of desired compounds from botanical materials. Its gentle evaporation process, coupled with vacuum assistance, ensures optimal extraction efficiency and preservation of heat-sensitive compounds. The applications of this method span across industries, from essential oil production to natural product isolation and cannabinoid extraction. By employing a rotary evaporator, researchers and industries can achieve time-efficient extractions, improved yields, and enhanced purity of the extracted substances. With its versatility and scalability, the rotary evaporators continues to be a vital tool in the field of plant extraction.
